Wednesday, February 24, 2010
Link Between Influenza Outbreaks and Humidity
Beginning observations in New York, Washington, Illinois, Arizona and Florida, then spreading to the rest of the continental U.S. Shaman and his colleagues discovered that the start of many influenza outbreaks during the winter came after a period of weather that was drier than usual. Shaman makes it a point to clarify that a dry period is not a necessary requirement to trigger an influenza outbreak, nor can the information help predict where there will be an influenza outbreak . However, this discovery could have a major impact on the development of strategies forlimiting spread of infection.
Sunday, February 21, 2010
Lacking Telomeres May Make You Age Faster
Scientists may have made a breakthrough in establishing the cause and speed of biological aging by researching telomeres. Telomeres are DNA pieces on the end of chromosomes which help protect the chromosomes from damage and degrading over time. They are almost padding or protection to the weak DNA inside of them. Some scientists now think that these shrinking as cells divide is the cause of biological aging. First, it is important to know the difference between biological and chronological aging. Biological aging is how your cells are physically after the splitting of these cells. Chronological age merely refers to how long you have actually lived. What these scientists are saying is that someone with smaller telomeres who has lived 45 years may actually have the body of a 55 year old individual.

The white pieces on the end are telomeres.
Source: http://www.scientificamerican.com/article.cfm?id=aging-telomere
Acknowledgements: Scientific American for writing the first article, and Nilesh Samani and the University of Leicester for conducting the research
Scorpion Venom Used to Cure Pain
The Israeli Yellow scorpion's venom works in the way that neurotoxin works. When the neurotoxins get inside the body, the they will almost instantly paralyze the prey preventing them from fleeing, and fighting back. The venom from the Israeli Yellow Scorpion is only affective on small prey, but when the venom is put inside a bigger animal, like a human, there is not as bad of an effect.
There are many dangerous things that need to be worked on right now in the new painkillers with venom in it. The scientists are dealing with the Israeli yellow scorpion which is one of the deadliest scorpions in the world. This scorpion is very poisonous. The Israeli yellow scorpion has 300 different peptides in its venom and only some of them have been researched. Many of the peptides' affects are unknown. There are also many dangers in the scorpion's toxins. Currently Prof. Gurevitz and other scientists are trying to produce these new painkillers with minimized problems of the venom's bad bioactive components.
Though this drug does have some side affects there are great things that can also come from this new pain killer. If the scientists were to successfully produce this painkiller it could solve one of the biggest problems in the medical world today. Aspirin does not help with extreme pain and morphine is an addictive drug. These new drugs would help with serious burns, bad cuts, would be a good thing to use in the military, and would be useful to people with bad injuries after earthquakes and other natural disasters. This new painkiller would work quickly, effectively, and there would be no addiction associated with the drug.


utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+sciencedaily+%28ScienceDaily%3A+Latest+Science+News%29&utm_content=Netvibes
-www.wilsonsbiologylab.com
-google docs
https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgc13vSPrXNd4s1wnw70JNJqA-hGZRCQqGmIOLLlWY2pNsdZ826aACAwjtWtYm-gvh-lH9XQy7HR4Su8saA30ZMY3I-ZuQNi0q094HjWCep-qMiW38XxpMc6g4m-6IyUJZtWCn9QN9H-qXJ/s200/arizona_bark_scorpion.jpg
http://files.turbosquid.com/Preview/Content_2009_07_14__00_07_03/scorpio.jpg92B9A1A1-299D-40C6-BBEA7F68FD4402EF.jpgLarge.jpg
- http://www.flightglobal.com/blogs/flight-international/scorpion.gif
Can dolphins help with diabetics?
Studies show that this "insulin resistance" that dolphins have can be bad. The insulin level in something is when cells in the liver, muscles, and fat tissue take glucose from the blood and keep it in the liver and muscles. From this resistance the dolphins could start to produce a "pathological form of diabetes," meaning there is no way for the diabetes to go away, and they cannot control it. For weeks scientists worked to study dolphin's insulin levels. They did this after each dolphin ate, and they studied six dolphins. They found that when dolphins fast, they "show changes in blood chemistry" and they also have changes in their glucose level, which is exactly like humans. Humans and dolphins are very different, but we both have big brains and large blood cells which can carry big amounts of glucose. Some scientists believe that humans have a similar "switch," like the dolphins, in our bodies. Scientists believe that after the ice age, humans could not eat carbs because all the foods with carbs froze. So, they believe that humans used this "insulin resistance" to keep glucose in the brain. They believe something similar to this happened to the dolphins many years ago. In conclusion, scientists think and hope that maybe they could find a diabetic "switch" in humans.
By, Raina, Irena, and Aliza
Friday, February 19, 2010

Attacking Cancer Cells With Hydrogel Nanoparticles
Researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology have found a new way to aid chemotherapy and lessen the dramatic effects it has on the body. They are using special apoptosis causing RNA (siRNA) to kill cells in the specific area where the cancer is. Therefore, this procedure can target just the cancerours cells and not kill non-cancerous cells like chemotherapy does. This newly discovered type of siRNA does not totally do the job of chemotherapy, but it can make chemotherapy more effective and therefore lessen the time chemotherapy is actually used. This siRNA inhibits the EGFR’s (Epidermal growth factor receptors). In cancerous cells there is an overabundance of EGFR, which causes cells to go through mitosis faster and more often, and it also inhibits the cells apoptotic function. By interfering with the EGFR, siRNA allows the cell to regain its apoptotic function and also stop the constant reproduction of new mutated, cancerous cells.
The siRNA cannot survive outside of the cell very long, since it denaturalizes.
 However, the researchers have also found a hydrogel that keeps the siRNA intact outside the cells and therefore can be safely transported into the cancerous cells. The hydrogel does another, more important job. If the siRNA is only released at one time the cancerous cell can recover its control over the EGFR and therefore the treatment would be ineffective. However, the hydrogel releases the siRNA slowly and constantly over a period of time, which allows the cell to either go through apoptosis or for the chemotherapy to kill the cell.
However, the researchers have also found a hydrogel that keeps the siRNA intact outside the cells and therefore can be safely transported into the cancerous cells. The hydrogel does another, more important job. If the siRNA is only released at one time the cancerous cell can recover its control over the EGFR and therefore the treatment would be ineffective. However, the hydrogel releases the siRNA slowly and constantly over a period of time, which allows the cell to either go through apoptosis or for the chemotherapy to kill the cell.Works Cited:
http://www.medgadget.com/archives/img/sirna.jpg
http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2010/02/100216140404.htm?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+sciencedaily+(ScienceDaily%3A+Latest+Science+News)&utm_content=Netvibes
http://www.odec.ca/projects/2005/thog5n0/public_html/Tumour.gif
Wednesday, February 10, 2010
Malaria Vaccine
And, it appears that one may have been found. Called FMP2.1/ASO2A, this vaccine targets the falciparum malaria strain, the most common and deadliest strain. How it works, is a protein, called AMA-1 affects the virus and causes it to be ineffective or makes it easier for the immune system to defeat – the exact mechanism was not explained. In addition to this protein, an adjuvant system, called ASO2, is utilized to increase immune system response so the immune system is more likely, and better able, to produce the antibodies that will fight of later infections. The vaccine is currently being used tested on a larger scale, from 100 children to 400 children and thus far there have been no adverse effects.
There are, however, some problems with this vaccine. First, it treats only one specific strain. While this is a big step, and researchers are hopeful it will be effective against other strains, these other strains are killing people as well and this vaccine may not help them. Also, malaria is a parasite, which means it does not behave like a disease caused by a virus or bacterium. Unlike many of these diseases, when symptoms of malaria abate, the parasite is still in the victim’s body and relapses occur. What happens to people who survive the first time, is their immune system develops an immunity to the disease which lessens the severity of these relapses. Decreasing the severity of the relapses is what this vaccine attempts to duplicate. The problem with this approach, is that if the parasite is genetically altered in anyway, it is still in the victims body and the changes will affect the victim immediately, rather than on the off chance they get bitten by a mosquito with the altered parasite.
University of Maryland Medical Center. "New Malaria Vaccine Is Safe and Protective in Children, Scientists Find." ScienceDaily 6 February 2010. 10 February 2010
Monday, February 8, 2010
Health Benefits from Vitamin D?
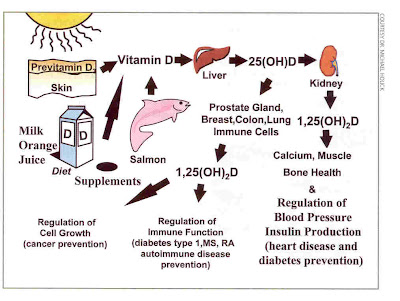
Acknowledgments:
Sunday, February 7, 2010
Will Genetic Juicing Replace Steroids?

Sea slugs that are half plant, half animal
Tuesday, February 2, 2010
Researchers find "broad spectrum" antiviral that fights multitude of viruses
One of the reasons viruses are near impossible to combat is the fact that not only do they vary in many ways but they mutate often. Deadly viruses such as HIV are able to resist so much of what is thrown at them because of their mutating abilities. Despite the mercurial nature of viruses a group of researchers from UCLA and other universities may have found an effective way to combat them.
The compound the researchers have discovered is a rhodanine derivative that the researchers have dubbed LJ001. It is classified as a “small molecule broad spectrum antiviral”, meaning that it fights viruses by attacking them through a common feature that viruses share. LJ001 works by binding to both cellular and viral membranes and inactivating them. However LJ001 is not harmful because of the natural regenerative qualities of metabolically active cells which are able to repair the damage unlike the virus cell. Therefore the compound is able to attack viruses without serious damage to the rest of an organisms’ cells. Researchers have seen the effectiveness of LJ001 on various virus strains however the exact mechanism if viral membrane inactivation is still unknown
One of the reasons for excitement over LJ001 is the fact that the FDA has approved few broad spectrum antivvirals, and the ones that have generally less effective and very costly. Studies have shown that LJ001 has the potential to be effective against a wide range of viruses HIV-1, influenza A, filoviruses, poxviruses, arenaviruses, bunyaviruses, paramyxoviruses and flaviviruses. These viruses are the cause of some of world’s deadliest diseases such as, Nipah virus encephalitis, Ebola, hemorrhagic fever and Rift Valley fever. Since it is a broad spectrum antiviral, LJ001 may even have the properties to be effective against viruses that have yet to be discovered.
Rivero, Enrique. "Researchers find 'broad spectrum' antiviral that fights multitude of viruses."www.eurekalert.org. 01/02/2010. Eurekalert, Web. 2 Feb 2010.
-Jukie & Cyrus
![Reblog this post [with Zemanta]](http://img.zemanta.com/reblog_e.png?x-id=c5e82790-7cb4-4d37-a08e-41d277e3cb4e)




